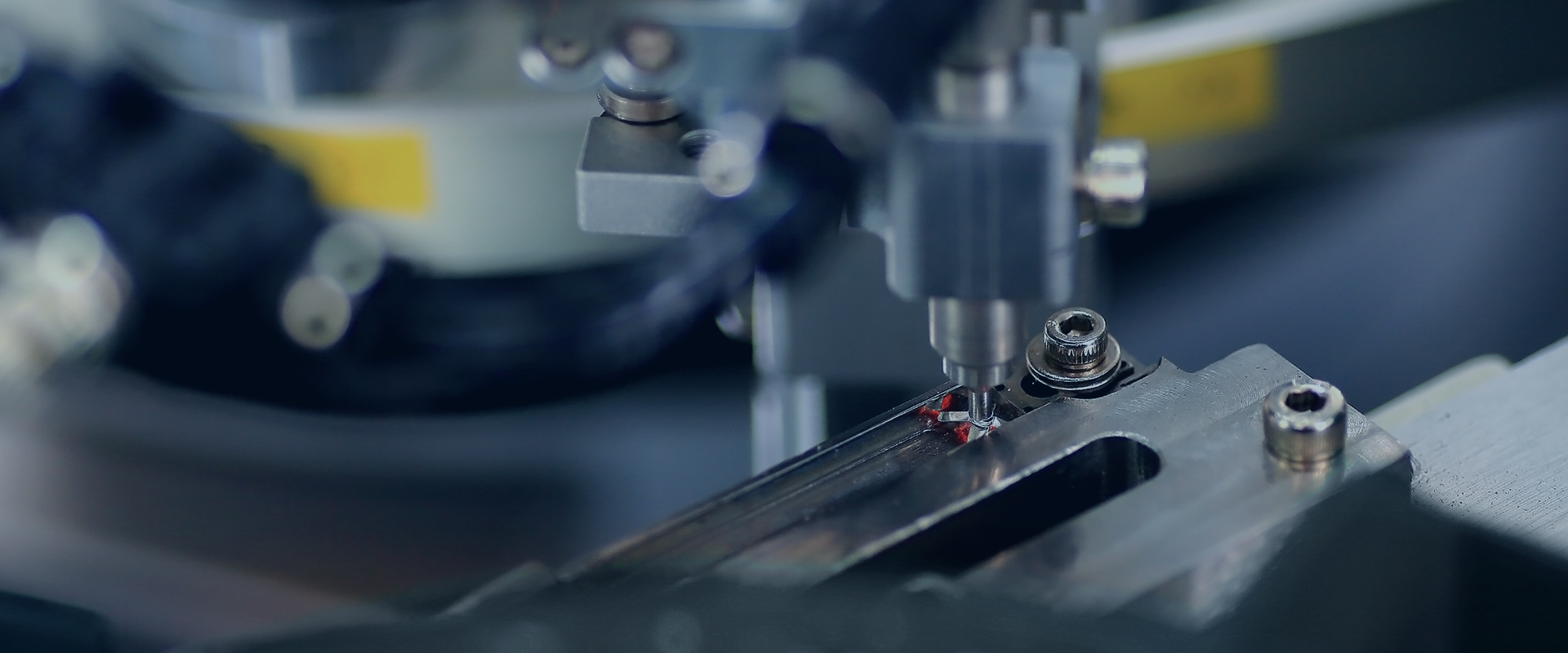
A thermal protection switch is a safety device designed to protect electrical equipment from overheating. It monitors the temperature of the device or its components and interrupts the electrical circuit when the temperature exceeds a predefined safe limit. This ensures the system operates within safe temperature ranges, preventing damage, equipment failure, or potential hazards such as fire.
Key Components of a Thermal Protection Switch
Temperature Sensor: Detects the heat generated by the equipment or surrounding environment. Common types include:
Bimetallic Strips: Two metals with different thermal expansion rates that bend or snap at a set temperature.
Thermistors: Temperature-sensitive resistors (NTC or PTC) that change resistance with temperature changes.
Thermocouples: Measure temperature based on voltage differences created by heat.
Switching Mechanism: Activates or deactivates the electrical circuit based on the sensor's input. This can be a mechanical or electronic relay.
Housing: Protects the internal components from environmental factors like dust, moisture, or vibrations.
Connection Terminals: Allow the thermal switch to integrate with the device’s electrical system.
How Does a Thermal Protection Switch Work?
Temperature Monitoring: The sensor monitors the temperature of the equipment or its environment.
Threshold Detection: When the temperature reaches the predefined limit, the sensor triggers the switching mechanism.
Circuit Interruption: The switch opens (or closes in some designs), cutting off power to prevent further temperature increase.
Resetting: Once the temperature returns to normal, some thermal switches automatically reset, while others require manual intervention.
Types of Thermal Protection Switches
Automatic Reset Switches:
Automatically reclose the circuit when the temperature returns to safe levels.
Common in household appliances like irons and hairdryers.
Manual Reset Switches:
Require user intervention to reset the switch after it’s triggered.
Used in critical systems to ensure issues are addressed before restarting.
One-Time Use Switches:
Permanently interrupt the circuit when activated, requiring replacement.
Found in devices where maximum safety is essential, like heaters and power supplies.
Electronic Thermal Protection Switches:
Use electronic components to detect and control temperature.
Offer high precision and are commonly used in modern electronics.
Applications of Thermal Protection Switches
Household Appliances:
Prevent overheating in irons, ovens, coffee makers, and hairdryers.
Industrial Equipment:
Protect motors, compressors, and transformers from excessive heat.
Automotive Systems:
Monitor engine temperatures and HVAC systems for safety and performance.
Medical Devices:
Ensure safe operation of sensitive equipment like MRI machines and surgical tools.
Electronics:
Safeguard laptops, chargers, and power supplies from overheating.
Renewable Energy Systems:
Used in solar inverters and wind turbines to prevent thermal damage.
Advantages of Thermal Protection Switches
Enhanced Safety: Prevents fires and accidents caused by overheating.
Prolonged Equipment Lifespan: Protects components from thermal stress and failure.
Energy Efficiency: Reduces unnecessary energy consumption by shutting down overheated systems.
Low Maintenance: Reliable performance with minimal upkeep required.
Cost-Effective: Prevents costly repairs and replacements due to thermal damage.
Selecting the Right Thermal Protection Switch
Temperature Range: Choose a switch with a suitable operating range for the application.
Reset Type: Determine whether automatic or manual reset is appropriate.
Load Capacity: Ensure the switch can handle the electrical load of the device.
Environmental Factors: Consider protection against moisture, dust, and vibrations.
Regulatory Compliance: Verify adherence to safety standards like UL, IEC, or RoHS.
A thermal protection switch is a crucial safety device that protects electrical systems and devices from overheating. By interrupting the electrical circuit when temperatures exceed safe limits, it prevents damage, enhances safety, and prolongs the lifespan of equipment. Understanding its operation, types, and applications can help in selecting the right switch for specific needs, ensuring reliable and safe operation across various industries.





 中文
中文 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano 한국어
한국어 にほんご
にほんご


