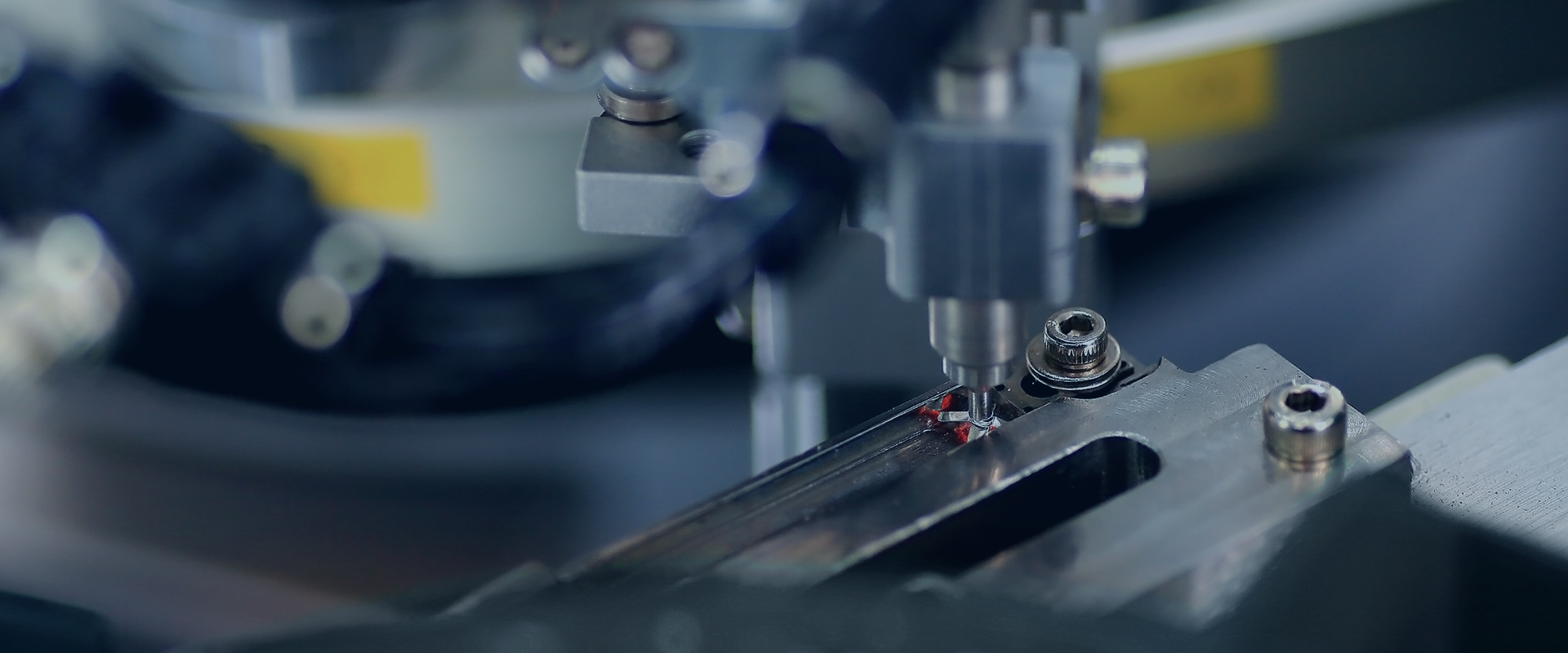
A thermal cutoff switch, also known as a thermal fuse, is a safety device designed to interrupt the flow of electricity in a circuit when the temperature exceeds a predefined threshold. This mechanism is widely used in electrical appliances, industrial equipment, and automotive systems to prevent overheating and potential fire hazards. Understanding how a thermal cutoff switch works can help in its proper application and maintenance.
Components of a Thermal Cutoff Switch
Temperature-Sensitive Element: A material that reacts to temperature changes, typically a fusible alloy or a bimetallic strip.
Electrical Contacts: Metal contacts that complete the electrical circuit when closed.
Housing: An insulating casing that protects the internal components and ensures safe operation.
Connection Terminals: Points where the switch is integrated into an electrical circuit.
Principle of Operation
The thermal cutoff switch operates based on the principle of thermal expansion or the melting of a temperature-sensitive element. When the ambient or component temperature rises beyond the specified limit, the switch activates to interrupt the current flow.
There are two primary mechanisms by which thermal cutoff switches operate:
1. Fusible Alloy Mechanism
A thermal cutoff switch with a fusible alloy contains a small pellet or solder that melts at a specific temperature.
Under normal operating conditions, the fusible alloy keeps the electrical contacts closed, allowing current to flow.
When the temperature exceeds the threshold, the alloy melts, causing the contacts to open and interrupt the circuit.
This type of thermal cutoff switch is typically non-resettable and must be replaced after activation.
2. Bimetallic Strip Mechanism
A bimetallic strip is made from two metals with different coefficients of thermal expansion.
As the temperature rises, the strip bends due to the differing expansion rates of the metals.
At the critical temperature, the bending motion separates the electrical contacts, breaking the circuit.
Some bimetallic thermal cutoff switches are resettable, either manually or automatically, once the temperature returns to safe levels.
Steps in Thermal Cutoff Switch Operation
Temperature Monitoring: The thermal element constantly monitors the ambient or device temperature.
Activation Threshold: If the temperature exceeds the predetermined limit, the thermal element reacts (melts or bends).
Circuit Interruption: The reaction causes the electrical contacts to open, stopping current flow.
System Protection: By breaking the circuit, the switch prevents further temperature rise and potential damage.
Reset (if applicable): In resettable models, the switch returns to its original state once the temperature normalizes. In non-resettable models, the switch must be replaced.
Applications of Thermal Cutoff Switches
Thermal cutoff switches are used in a variety of applications, including:
Household Appliances:
Hairdryers, toasters, coffee makers, and heaters to prevent overheating.
Industrial Equipment:
Motors, transformers, and heating elements for temperature regulation and safety.
Automotive Systems:
Engine temperature monitoring and HVAC systems to ensure safe operation.
Electronics:
Power supplies and chargers to prevent overheating and component damage.
Medical Devices:
Used in sensitive equipment to ensure reliable and safe operation.
Advantages of Thermal Cutoff Switches
Safety: Protects devices and users from overheating and potential fire hazards.
Reliability: Designed for precise operation at specific temperature thresholds.
Low Maintenance: Typically requires minimal upkeep and is easy to replace in non-resettable models.
Compact Design: Small size allows integration into a wide range of devices.
Maintenance and Precautions
Regular Inspection: Periodically check the switch for signs of wear or damage.
Proper Replacement: Use a thermal cutoff switch with the correct temperature rating when replacing a failed unit.
Avoid Overloading: Ensure the device operates within the specified voltage and current ratings to prevent premature activation.
A thermal cutoff switch is a critical safety component that protects electrical systems from overheating and ensures safe operation. By understanding its working principle—whether through fusible alloy or bimetallic mechanisms—users and engineers can effectively implement these devices in various applications. Proper maintenance and adherence to temperature and voltage specifications further enhance their performance and longevity.





 中文
中文 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano 한국어
한국어 にほんご
にほんご


