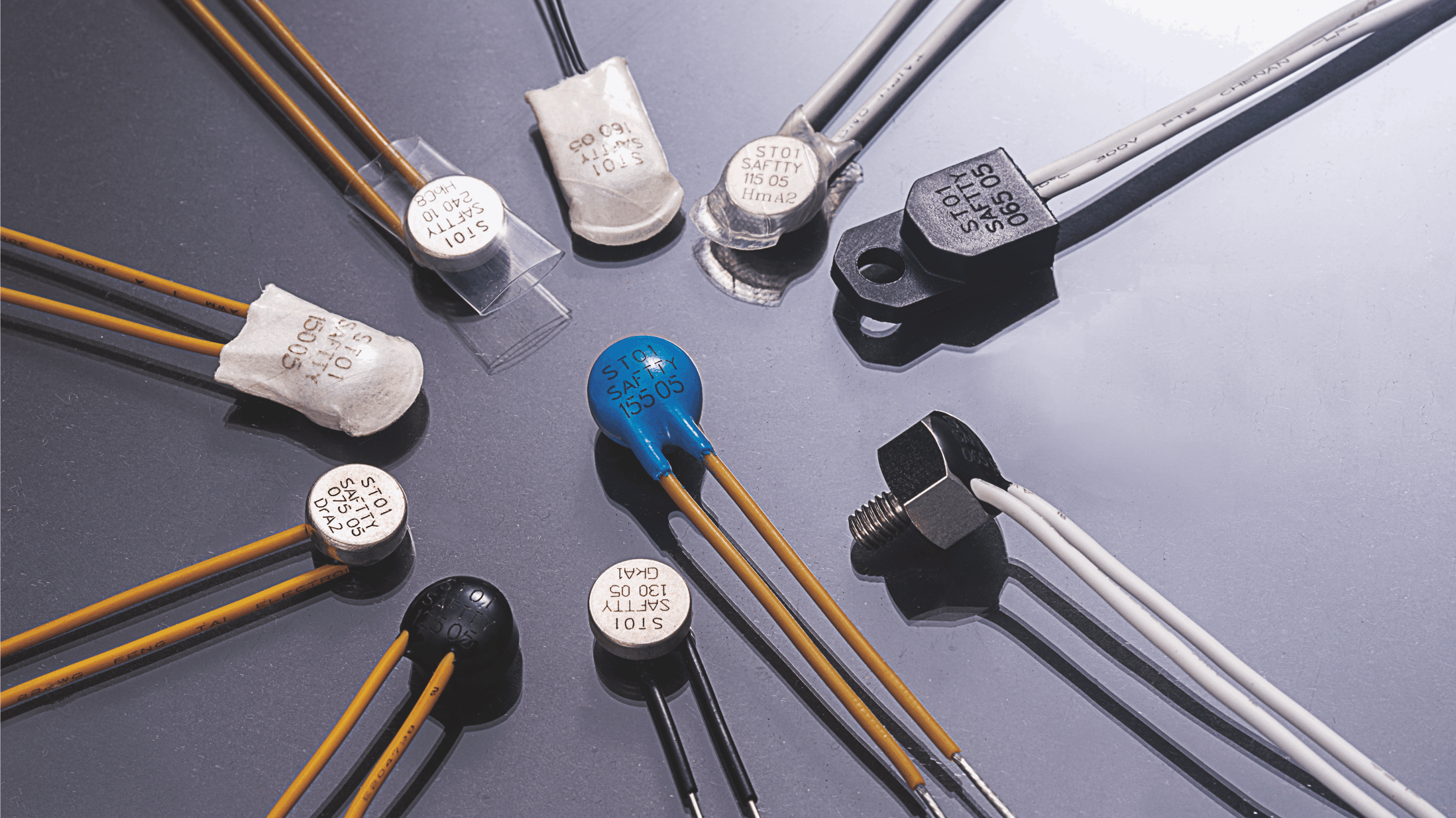
Thermal protectors are essential components in various electrical and electronic systems, ensuring the safe operation of devices by preventing overheating. These protectors are widely used in applications ranging from household appliances to industrial equipment.
Bimetallic Thermal Protectors
Bimetallic thermal protectors are among the most commonly used types of thermal protectors. They operate based on the principle of thermal expansion. These protectors consist of two different metals with varying coefficients of thermal expansion, bonded together. When heated, the metals expand at different rates, causing the bimetallic strip to bend. This bending action can trigger a switch or a relay to interrupt the electrical circuit, thereby preventing further heating.
Applications: Bimetallic thermal protectors are widely used in household appliances such as hair dryers, toasters, and refrigerators. They are also employed in HVAC systems to maintain temperature within a specified range.
PTC Thermistors
PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) thermistors are another type of thermal protector. These devices exhibit a sharp increase in electrical resistance as the temperature rises. When the temperature exceeds a certain threshold, the resistance of the PTC thermistor increases significantly, limiting the current flow through the circuit. This mechanism effectively protects the circuit from overheating.
Applications: PTC thermistors are commonly used in applications where overcurrent protection is required, such as in power supplies, motor windings, and battery packs. They are also used in temperature sensors and as heating elements in some devices.
Thermal Fuses
Thermal fuses are designed to provide a one-time, irreversible cutoff of electrical current when the temperature exceeds a specified limit. These fuses are typically made from a fusible link that melts at a predetermined temperature, breaking the circuit. Once activated, thermal fuses cannot be reset and must be replaced.
Applications: Thermal fuses are commonly used in applications where safety is paramount, such as in electric motors, heaters, and other devices that are prone to overheating. They are also used in consumer electronics like hair dryers, irons, and coffee makers to prevent fire hazards.
Working Principles
Bimetallic Thermal Protectors: The working principle of bimetallic thermal protectors involves the differential expansion of two metals. When the temperature rises, the bimetallic strip bends due to the different expansion rates of the metals. This bending action can trigger a switch or relay to cut off the power supply.
PTC Thermistors: PTC thermistors work by increasing their resistance sharply as the temperature rises. This increase in resistance limits the current flow, preventing the circuit from overheating. The resistance of a PTC thermistor is highly temperature-dependent, making it an effective thermal protector.
Thermal Fuses: Thermal fuses operate by melting a fusible link when the temperature exceeds a set threshold. This melting action breaks the circuit, cutting off the electrical current. Once activated, thermal fuses are non-resettable and must be replaced.
Considerations for Selection
When selecting a thermal protector, several factors must be considered:
Operating Temperature Range: Ensure that the thermal protector operates within the temperature range required by the application.
Current Rating: The thermal protector should be able to handle the current levels of the circuit without premature activation.
Response Time: The response time of the thermal protector should be appropriate for the application. Some applications may require faster response times to prevent damage.
Reset Capability: Determine whether a resettable or non-resettable thermal protector is more suitable for the application. Resettable protectors can be reused, while non-resettable protectors must be replaced after activation.
Thermal protectors play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and reliable operation of electrical and electronic devices. Bimetallic thermal protectors, PTC thermistors, and thermal fuses each offer unique advantages and are suited to different applications. By understanding the working principles and selecting the appropriate type of thermal protector, engineers and technicians can enhance the safety and performance of various systems. Whether used in household appliances, industrial equipment, or consumer electronics, thermal protectors are indispensable components in modern electrical systems.










 中文
中文 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano 한국어
한국어 にほんご
にほんご


