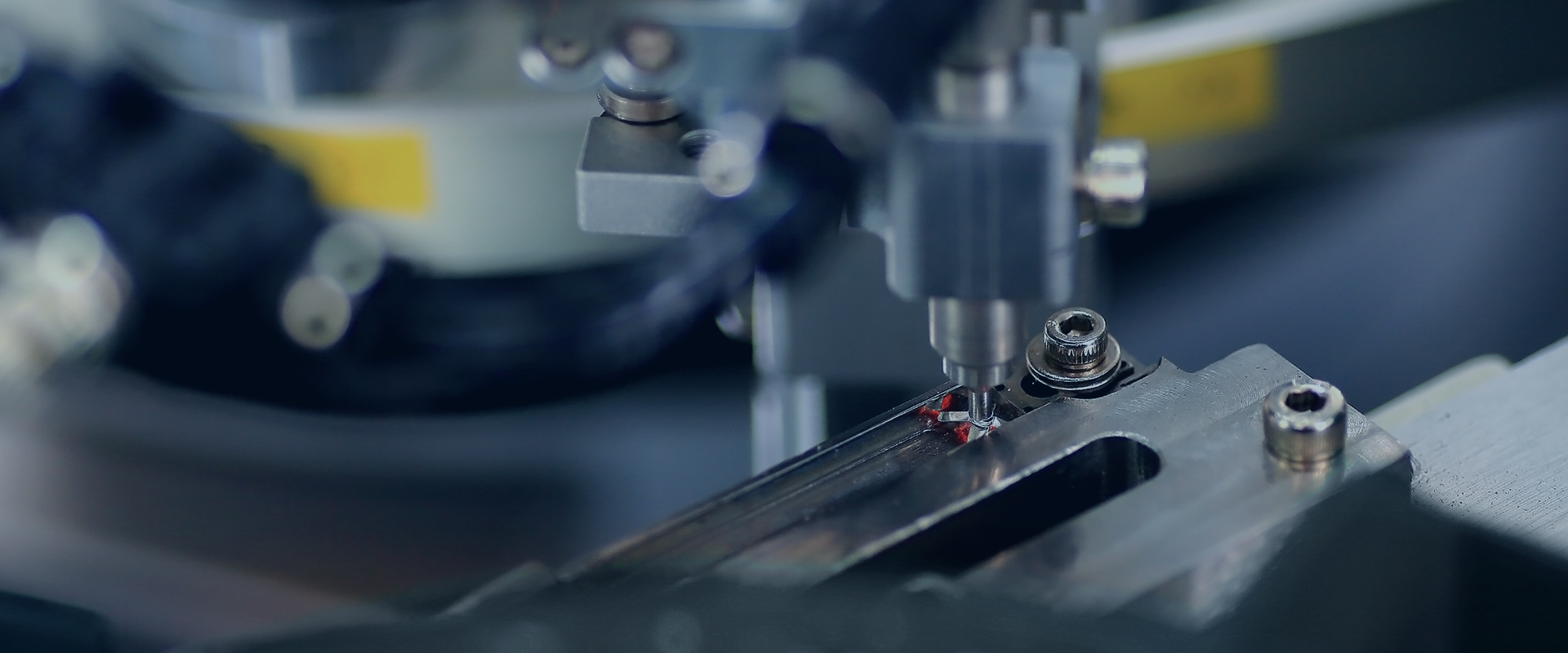
Thermal protection is a safety mechanism designed to prevent electrical devices and systems from overheating, which can lead to equipment failure, reduced lifespan, or hazardous conditions like fires. The system detects excessive temperatures and takes corrective action to protect the equipment. Here's an in-depth look at how thermal protection works:
Key Components in Thermal Protection Systems
1. Temperature Sensors: Devices such as thermistors, thermocouples, or resistance temperature detectors (RTDs) measure the temperature of the equipment or environment.
2. Control Circuit: Processes the temperature data and decides whether protective action is needed.
3. Thermal Protectors (e.g., Thermal Overload Protectors): Specialized devices that directly interrupt the electrical circuit if the temperature exceeds a safe threshold.
4. Cooling Systems: Fans, heat sinks, or liquid cooling mechanisms that help manage excessive heat.
Working Mechanism of Thermal Protection
1.Monitoring Temperature:
Temperature sensors or bimetallic strips continuously monitor the operating conditions of the equipment.
The system compares the real-time temperature with a predefined safe threshold.
2.Detecting Overheating:
If the temperature rises beyond the safe limit due to excessive current, environmental conditions, or prolonged use, the thermal protection system is triggered.
3.Protective Action:
Circuit Interruption: A thermal protector may break the electrical circuit to stop power flow and prevent further heating.
Cooling Activation: The system may activate fans or pumps to dissipate heat.
System Shutdown: In advanced systems, thermal protection can shut down the entire device or system safely to prevent damage.
4.Resetting the System:
Automatic Reset: Once the temperature returns to normal, the system automatically resumes operation.
Manual Reset: Some systems require manual intervention to restart the equipment after the issue is resolved.
Applications of Thermal Protection
Thermal protection systems are widely used in various industries and devices, including:
1. Electric Motors: To prevent overheating during high-load conditions.
2. Transformers: To ensure safe operation under varying electrical loads.
3. Medical Devices: To protect sensitive equipment like ventilators and imaging systems.
4. Batteries and Chargers: To avoid overheating during charging cycles.
5. Industrial Equipment: To maintain safe operation in high-temperature environments.
Benefits of Thermal Protection
1. Equipment Safety: Prevents damage to sensitive components.
2. Fire Hazard Reduction: Minimizes the risk of fire due to overheating.
3. Extended Lifespan: Protects devices from thermal stress, increasing their longevity.
4. Operational Reliability: Ensures consistent performance even under demanding conditions.
5. Energy Efficiency: Helps maintain optimal temperature levels, reducing energy wastage.
Types of Thermal Protection Devices
1.Thermal Overload Protectors:
Used in motors and transformers.
Break the circuit when a temperature limit is exceeded.
2.Thermistors:
Temperature-sensitive resistors that adjust electrical resistance based on heat levels.
One-time use devices that permanently open the circuit if a critical temperature is reached.
4.Integrated Circuit (IC) Thermal Sensors:
Common in modern electronics for real-time temperature monitoring.
Thermal protection is an essential feature in modern electrical and electronic systems, ensuring safety, reliability, and efficiency. By monitoring and managing heat levels, thermal protection systems prevent overheating-related failures and extend the lifespan of devices. Whether in industrial machinery, consumer electronics, or critical medical equipment, thermal protection safeguards both equipment and users from potential hazards.





 中文
中文 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano 한국어
한국어 にほんご
にほんご


