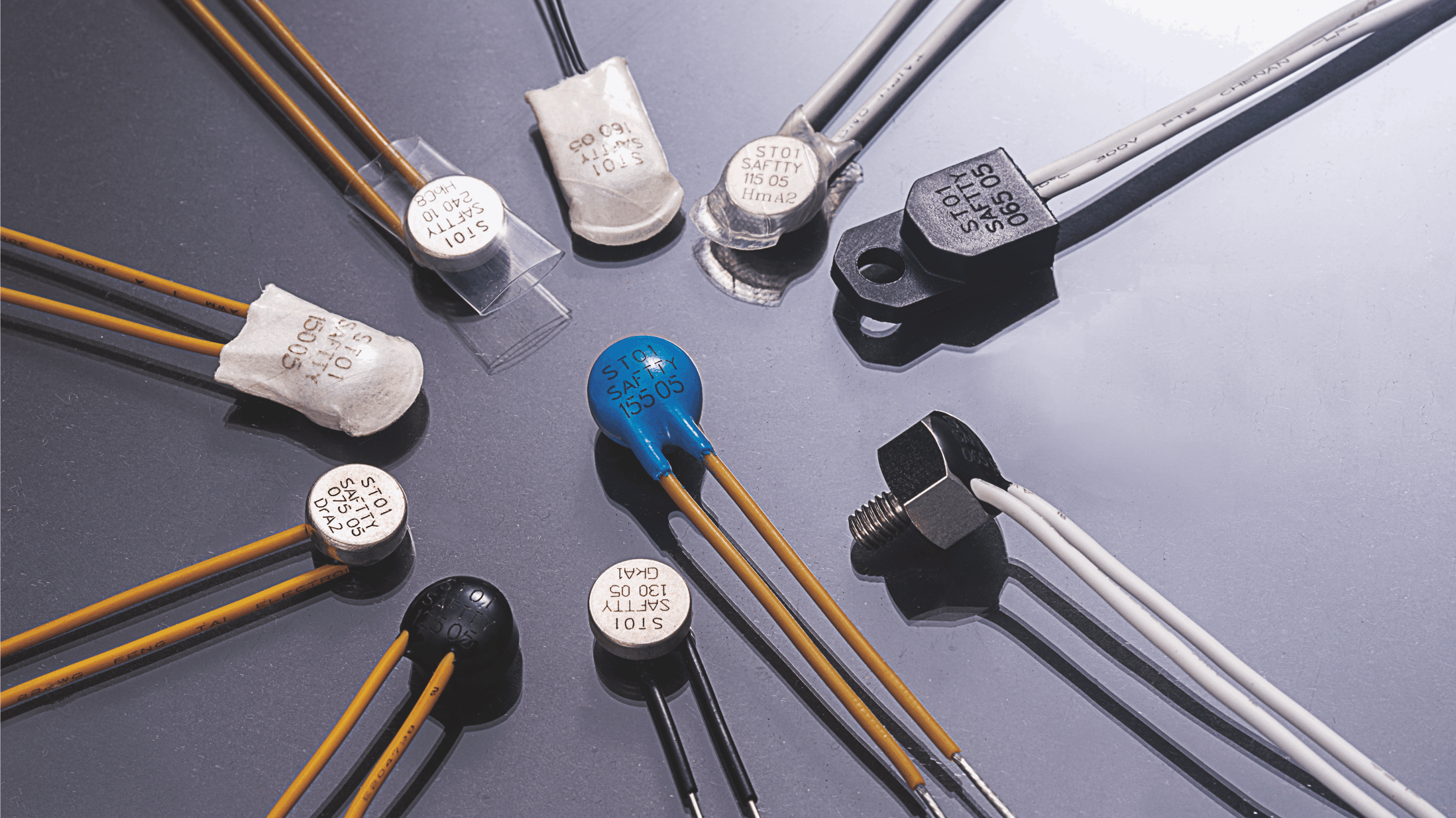
A thermal overload protector is a safety device designed to protect electrical equipment and circuits from overheating caused by excessive current or prolonged operation under high thermal conditions. Here's an overview of how it works:
Components of a Thermal Overload Protector:
1. Bimetallic Strip: The core component made of two metals with different expansion rates when heated.
2. Contacts: Conduct electricity when the protector is in a closed state.
3. Housing: Encases and insulates the protector.
4. Reset Mechanism (optional): Manual or automatic reset feature after tripping.
Working Principle:
1.Normal Operation:
Under normal current flow, the thermal overload protector remains inactive, and the circuit operates uninterrupted. The bimetallic strip stays stable and keeps the contacts closed, allowing electricity to pass.
2.Overload Condition:
When the current exceeds the safe limit or the temperature rises due to prolonged operation or a fault (like a short circuit or mechanical blockage), the bimetallic strip heats up.
The heat causes the two metals in the bimetallic strip to expand at different rates, bending the strip.
3.Circuit Interruption:
The bending of the bimetallic strip forces the contacts to open, breaking the electrical circuit.
This stops the current flow, protecting the equipment from damage due to overheating.
4.Resetting the Protector:
Automatic Reset: Once the device cools down, the bimetallic strip returns to its original shape, closing the contacts and restoring the circuit.
Manual Reset: Some protectors require a manual action to reset the circuit after tripping.
Applications:
Thermal overload protectors are used in:
· Electric Motors: To prevent overheating in industrial and home appliances.
· Transformers: To safeguard against excessive heat from overloads.
· Power Supplies: To ensure safe operation in sensitive electronic systems.
· Medical Devices: To maintain operational reliability and patient safety.
· Fans and Pumps: To avoid motor burnout.
Advantages:
· Prevents damage to expensive equipment.
· Reduces fire risk from overheated electrical components.
· Enhances the longevity of devices by avoiding thermal stress.
By monitoring and responding to heat buildup, thermal overload protectors play a critical role in maintaining safety and reliability in electrical systems.





 中文
中文 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano 한국어
한국어 にほんご
にほんご


