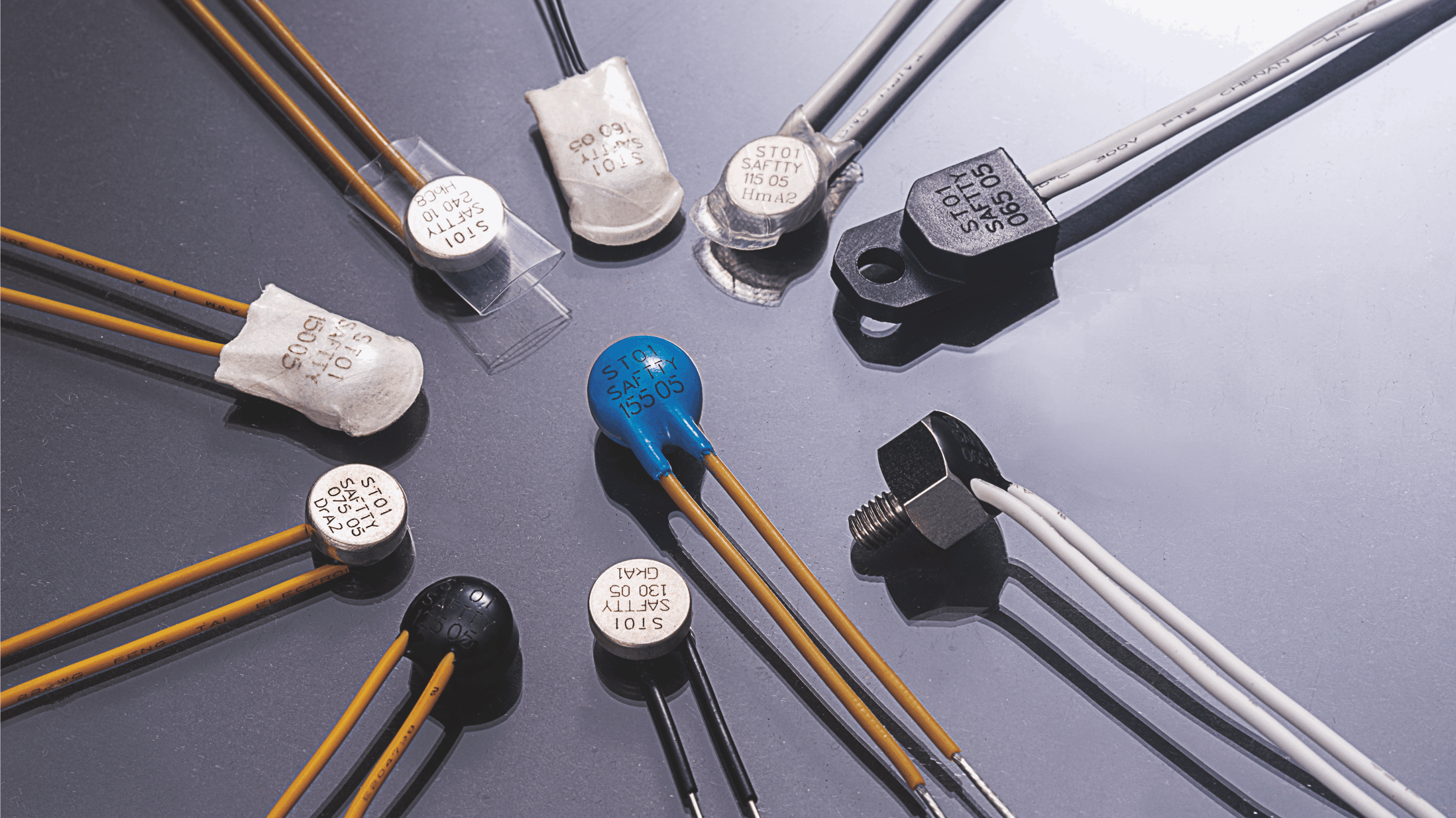
PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) thermal protectors are devices designed to safeguard electrical and electronic equipment by preventing overheating. Their operation is based on the unique properties of PTC materials, which exhibit a sharp increase in electrical resistance when their temperature rises beyond a specific threshold. Here's a detailed explanation of how they work:
Key Components
1. PTC Element: A material (typically a polymer or ceramic) with a temperature-sensitive resistance characteristic.
2. Housing: Encases the PTC element to provide mechanical stability and insulation.
3. Electrical Contacts: Allow integration into the electrical circuit.
Working Mechanism
1.Normal Operation:
At normal temperatures, the PTC element has low resistance, allowing electrical current to flow freely.
The circuit operates efficiently without significant heat generation from the PTC protector.
2.Temperature Rise:
If the temperature in the circuit or surrounding environment rises due to factors like excessive current, mechanical failure, or environmental heat, the PTC element starts to heat up.
Once the temperature reaches the trip point (a pre-defined threshold temperature), the PTC material undergoes a phase transition that dramatically increases its resistance.
3.Circuit Interruption:
The sudden resistance spike reduces the current flow to negligible levels, effectively limiting power delivery and protecting the circuit components from damage.
This action helps to prevent overheating, fires, or other catastrophic failures.
4.Automatic Reset:
Once the fault condition is resolved and the PTC element cools down, it reverts to its low-resistance state.
The circuit resumes normal operation without the need for manual intervention, making PTC thermal protectors reusable and highly reliable.
Advantages
· Self-Resetting: Unlike traditional fuses, PTC protectors do not require replacement after tripping.
· Durability: Can endure multiple overcurrent or overtemperature cycles.
· Compact Size: Ideal for modern electronic devices with space constraints.
· Wide Applications: Used in a variety of devices, including motors, transformers, heating systems, battery packs, and consumer electronics.
Applications
1. Motors and Transformers:
o Protect against prolonged overcurrent conditions.
2. Battery Packs:
o Prevent overheating during charging or discharging.
3. Heaters and Hair Dryers:
o Maintain safe operating temperatures.
4. Medical Devices:
o Ensure reliability and safety in critical applications.
PTC thermal protectors combine simplicity, reliability, and effectiveness, making them a vital component in safeguarding electrical and electronic systems.





 中文
中文 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano 한국어
한국어 にほんご
にほんご


